Lesson 9. Develop of digital contents: GIMP
- Obtener enlace
- X
- Correo electrónico
- Otras aplicaciones
17.03.21
THEORICAL PART
In this lesson we will learn how to use digital technology in an innovative and creative way for our teaching.
Multimedia it is made up of text, images, graphics, videos, animations, sounds and / or any other media that can be processed digitally, using a computer system as support, through which these elements are presented. To correctly use multimedia we need to learn to distinguish between the different types of media available.
We have the digital multimedia (Text, Images, Graphics, Videos, Animations, Sounds) and the Interactive multimedia (User, Interaction, Examples: test, social networks, etc).
- Pixel-based: Each pixel is assigned a color. The image quality is linked to the resolution (number of information points per inch that are captured from the image), so the higher the resolution the better the image quality will be.
- Vector images: Originating from shapes (bézier curves, polygons, which have different associated attributes) defined mathematically, they are independent of the resolution, therefore when increasing their size they will not suffer pixel effect.
Images can also come in different formats:
- Bitmat formats: JPG, GIF, PNG, TIFF, RAW, BMP, PSD...
- Vector formats: PDF, PS, EPS, SVG and AI
We also saw some video formats (MPEG H.264, MPEG-4, DIVX, FLVo SWF, AVI, WMV, 3GP, XVID, etc) and sound formats (WAV and AIFF, FLAC - free, ALAC, APE, MP3, AAC, OGG vorbis - free, WMA, etc).
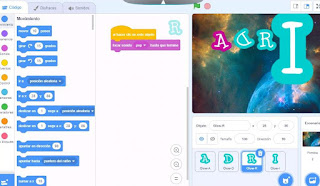
PRACTICAL PART
In today's practice, we had to create a post containing the images created in the 2 previous exercises, therefore we had to edit 3 images with GIMP:
- Obtener enlace
- X
- Correo electrónico
- Otras aplicaciones





Comentarios
Publicar un comentario